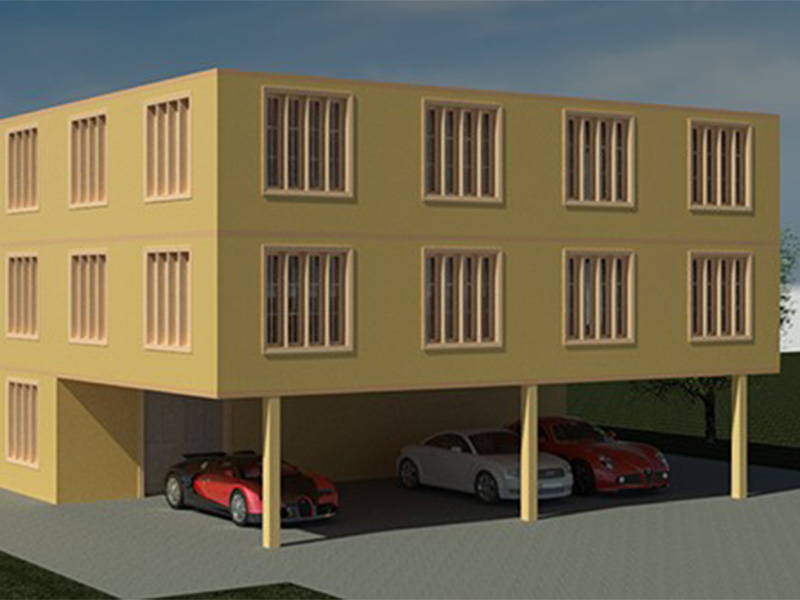
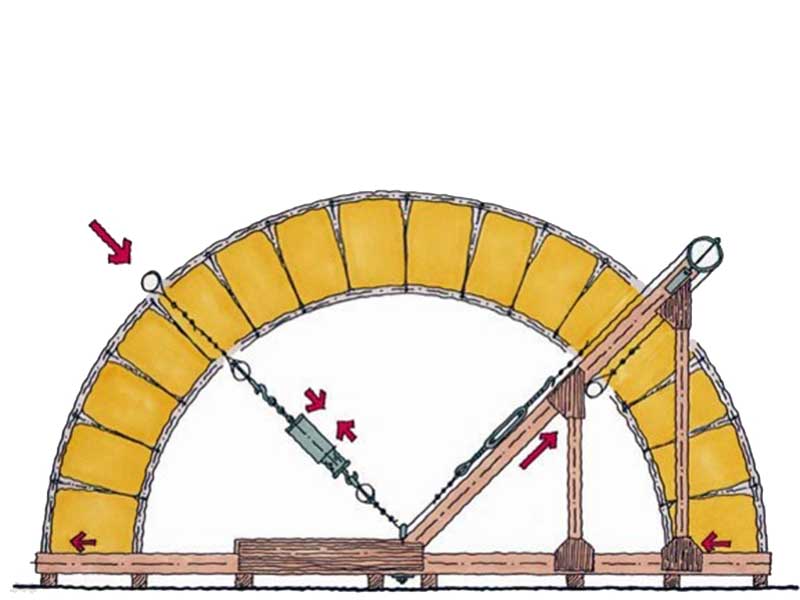
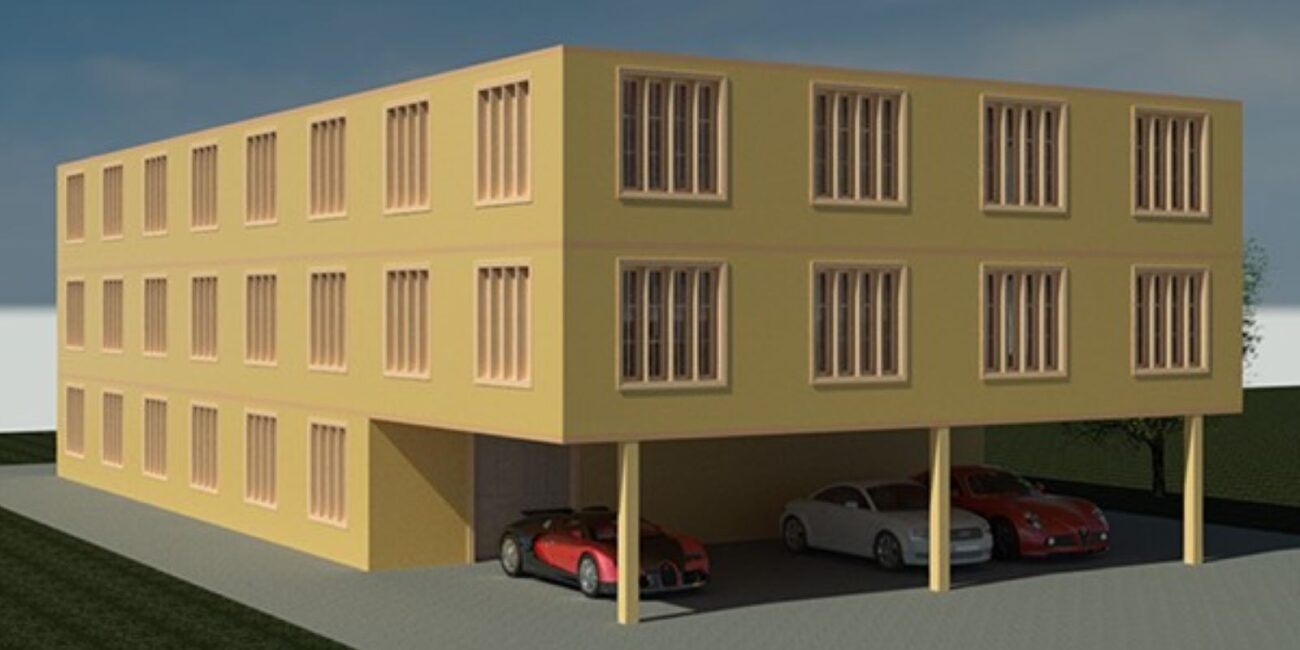
Retrofit of Multi-Unit Wood-Frame Buildings with Weak First Stories

Credit:
- Justin Moresco, PE, Director of Projects, Applied Technology Council
- David Mar, SE, Partner, Mar Structural Design
Published: Structure Magazine, July, 2024
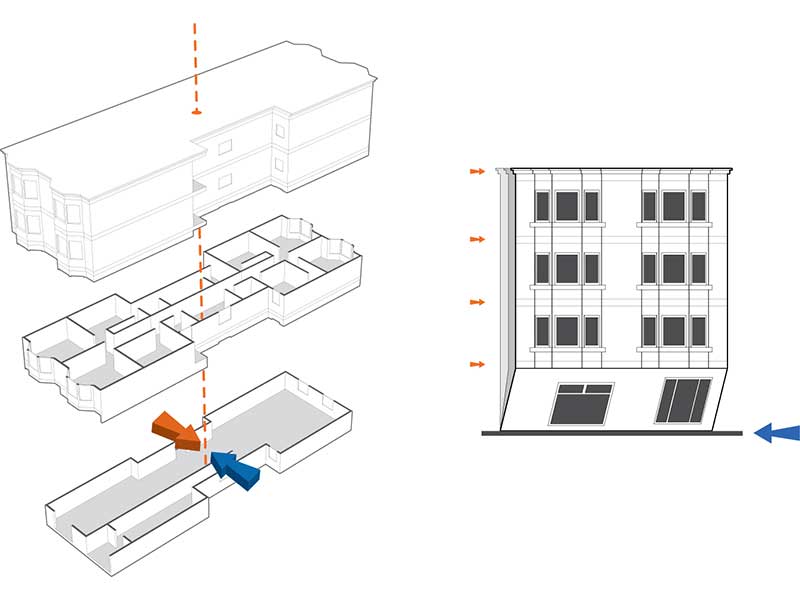
This article discusses recommendations from the FEMA P-807-1 report, which addresses retrofit strategies for improving the seismic performance of vulnerable soft, weak, or open-front (SWOF) wood-frame apartment buildings. These buildings, constructed from the 1950s to 1970s, are especially vulnerable to collapse during earthquakes due to weak lateral load-resisting systems. FEMA P-807 and its updated FEMA P-807-1 guidelines offer retrofit methodologies that strengthen the first story to reduce collapse risk while maintaining cost efficiency. Analytical studies show that ground floor retrofits, like those outlined in FEMA P-807, significantly lower collapse probabilities compared to simpler Line retrofits, which yield inconsistent results. The findings of FEMA-P-807-1 are timely because municipalities, particularly in California, have adopted retrofit ordinances targeting this typology in high-risk areas. These efforts aim to reduce the seismic risk posed by SWOF buildings, protecting public safety and minimizing post-disaster recovery costs. The guidelines balance the need for seismic resilience with practical considerations like cost, performance, and structural feasibility.
Related Research

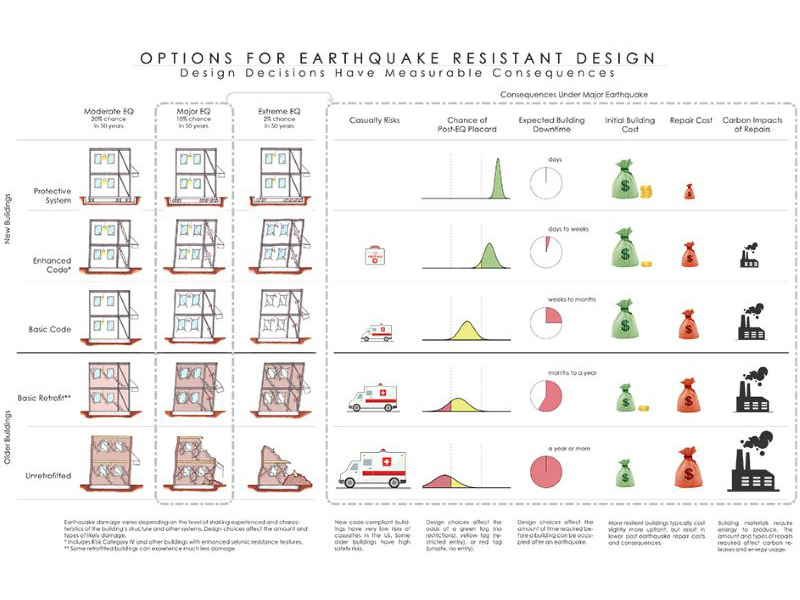
FEMA P-58: Options For Earthquake Resistant Design

Conceptual Seismic Design Guidance for New Reinforced Concrete Framed Infill Buildings

Earthquake Safety Prioritization of School Buildings Using Performance-Based Risk Assessment in Kyrgyz Republic
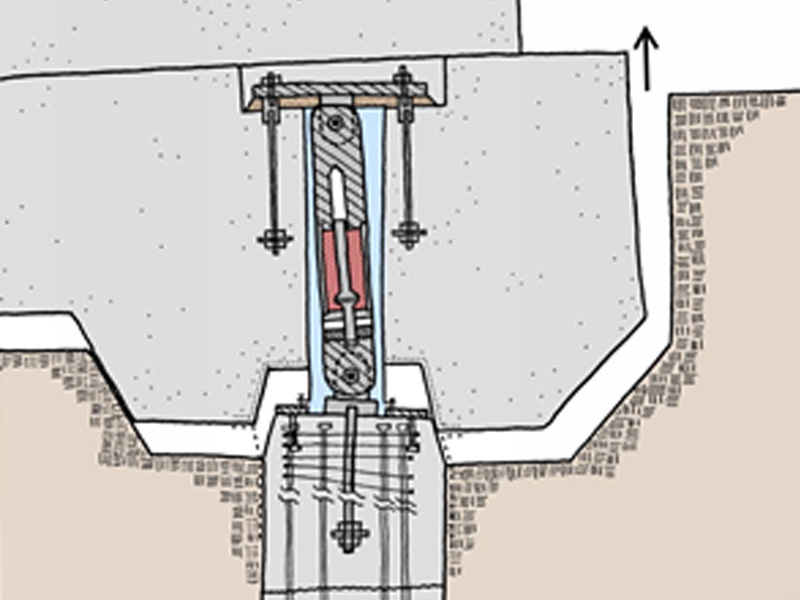
Casa Adelante: Rocking Mat Foundation System
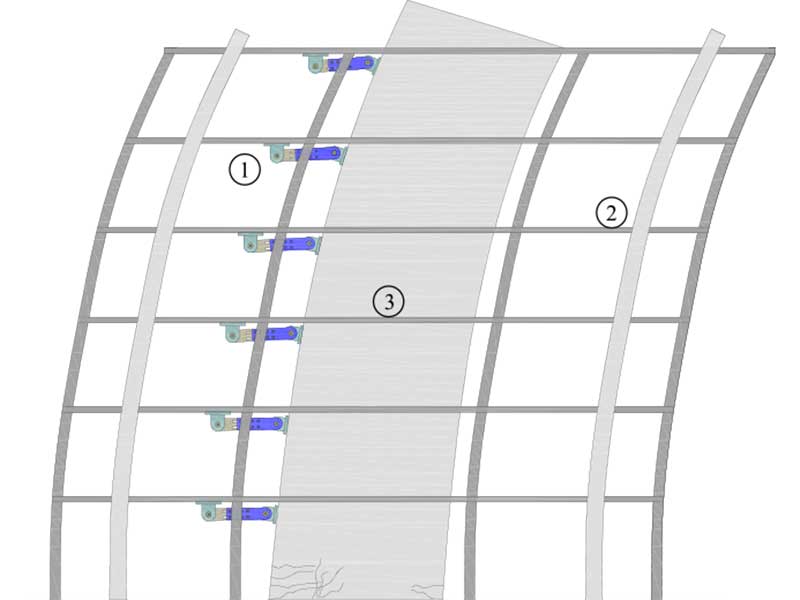
Development of Deformable Connection for Earthquake-Resistant Buildings to Reduce Floor Accelerations and Force Responses
FEMA P-807: Guidelines for Seismic Retrofit of Weak-Story Wood-Framed Buildings
Design Examples Using Mode Shaping Spines for Frame and Wall Buildings
Recommended Mesh Anchorage Details for Straw Bale Walls
Reversed Cyclic In-plane Tests of Load-bearing Plastered Straw Bale Walls